How to Automate Operations Without Breaking the Bank
Research reveals five factors that can drive automation costs up — or down.
News
- UAE Banks Phase Out OTPs Amid Fraud Surge
- Data Leak at Abu Dhabi Finance Week Exposes Details of 700+ Delegates
- Alibaba’s Latest Open-Weight Qwen3.5 Enters a Crowded Field
- MBZUAI Secures $1M from Google.org to Narrow AI’s Language Divide
- UAE Emerges as Global Powerhouse, 42% of Firms Named ‘AI Leaders’
- Riyadh Launches Automated Traffic Compensation Under Osool Program

Carolyn Geason-Beissel/MIT SMR | Getty Images
MANY EXECUTIVES at small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) associate process automation with expensive robots and assume that it’s within reach only for large enterprises. However, possibilities for reducing the amount of human involvement in tasks extend well beyond robots and include a host of affordable approaches. In our research with SMEs, we have uncovered strategies that can make automation feasible, even for businesses with lean budgets.
Consider how some SMEs have successfully implemented low-cost automation solutions in their production lines using barcode scanners and single-board computers to track order progress in real time. These solutions enable managers to provide updated information to sales and customer service personnel and to quickly react to potential delays — all for a technology investment that is often less than $300. Yet, most SMEs do not know where to start with automation or how to do it under their budget constraints and sometimes limited bandwidth for operational innovations.
Failure to embrace automation can put SMEs at risk of being less competitive. Our research with SMEs at Cambridge University’s Distributed Information and Automation Lab and MIT’s Supply Chain Digital Transformation Lab has revealed ways that smaller companies can start their automation journeys with a cost-effective approach. We’ll explore two strategies in particular: finding opportunities to automate peripheral functions, and looking for processes where stand-alone automation may offer benefits. And we’ll provide a framework for assessing the most cost-effective path for either strategy.
Why Peripheral Automation Can Be Cost-Effective
Many SMEs believe that automation yields benefits only if deployed in core activities such as production, which often require high levels of customization and must be highly reliable. One SME in the logistics delivery sector struggled to automate its core vehicle-routing process because the routing algorithms had to be extensively customized to accommodate a heterogeneous fleet, specific time windows, and backhauling, among other operational needs. But peripheral activities, such as monitoring work progress, can often be automated using sensors, actuators, cloud technology, and visualization platforms.1 These technologies are typically affordable, which gives them a significant advantage over technologies for automating core logistics activities such as order picking, whose costs can range from a few thousand to millions of dollars.2
For example, U.K.-based freight forwarder Meachers Global Logistics successfully automated a container-unloading monitoring process by using low-cost auto-ID tracking technologies. The company employed QR codes and smartphones alongside an open-source visualization platform to customize the interpretation of the results. This simple solution required no dedicated investment in technology components and enabled the company to react to unloading delays quickly, improving operational timeliness by 15%.
Data generated from automating peripheral activities can also enhance core activities by yielding insights for process improvement. Kemdent, a British manufacturer of dental materials, automated the monitoring of wax temperatures, which helped to optimize its modeling-wax production process. By linking temperature sensor data to issues observed with the wax, the company gained valuable insights into the optimal temperatures for producing modeling wax of the desired quality, and it improved production efficiency.3
Employ Stand-Alone Automation for Scalable Deployment
During our research with SMEs, several managers expressed concerns about the time and complexity of integrating automation into their operations. For instance, implementing order-picking robots in a warehouse often requires significant integration with the existing IT infrastructure.
Our research suggests that automation solutions that do not require full IT integration are more practical for SMEs because implementation is streamlined.4 Logistics provider CBW (Amco) adopted a stand-alone AI-based solution for its very narrow aisle (VNA) trucks. It installed internet-of-things vibration sensors on the trucks and applied an off-the-shelf machine learning algorithm (a Bayesian classifier), trained with labeled examples, to classify their vibration patterns into productive and unproductive states. This enabled them to determine the utilization of their VNA trucks in near real time, improving resource allocation by 11%. The solution was fast to implement because it did not require integration with company IT systems.5
Another benefit of stand-alone solutions is that many can be adopted incrementally. Companies can start with a simplified solution and later add capacity, or adopt full solutions one at a time and eventually interconnect them. For example, Amco started with a limited set of VNA trucks, but the solution was designed to make it easy to add new sensors and trucks if needed, and the off-the-shelf IoT sensors could share information with other systems if the company eventually needed to create a more interconnected solution. Provided that modularity and compatibility are considered at the outset, a company can adopt a basic version of stand-alone automation and scale it as resources allow and future opportunities arise.
Many AI applications fall into the category of flexible, stand-alone solutions that can be used for operations automation. For example, an SME that provided local logistics services to bottling company Coca-Cola Femsa used an AI chatbot to automate its workforce planning tasks.6 The AI-driven chatbot’s all-in-one functionality allowed it to receive data directly from the user, handle the planning problem by itself, export the results, and even share those results with other company systems through its available APIs, when necessary. As a result, the SME reduced errors in resource allocation and enhanced its efficiency.
Assessing the Cost Implications of Automation Factors
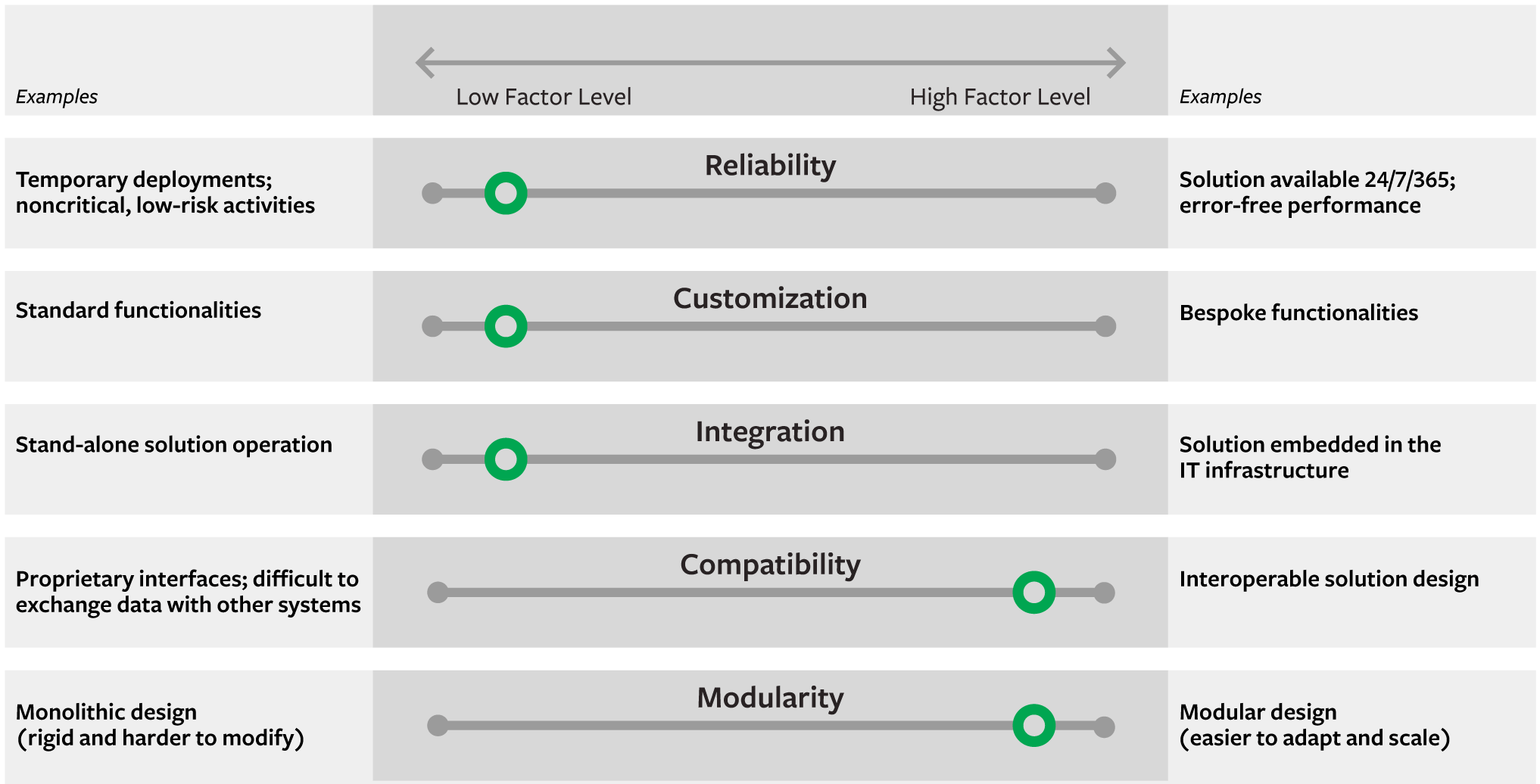
Green circles indicate where low or high levels of each factor lead to the most cost-effective automation solution. For example, a lower reliability factor is sufficient for noncritical activities and is associated with lower deployment costs. Modest reliability and customization requirements are most important when considering a peripheral automation strategy; low integration requirements, high compatibility, and high modularity are most important when considering a scalable stand-alone automation strategy.
A Framework for Cost-Effective Automation
As SMEs set out to pursue the strategies described above, they will need to evaluate specific use cases and will be required to implement them. To help with this, we’ve developed a framework that emphasizes the factors that affect the costs of the proposed strategies. (See “Assessing the Cost Implications of Automation Factors.”) The framework serves as a visual guide that highlights the key cost-related automation factors outlined below.
Reliability. When investing in an automation solution, identify the criticality of the process you intend to automate. Core processes require a high level of automation reliability; hence, the automation solution needs to perform flawlessly for long periods, which can increase costs. Peripheral processes, like monitoring operations, are more fertile ground for low-cost automation because of the lower demands for reliability.
Customization. Tailored solutions may be needed to provide the necessary functionality. Avoid investing in excessive customization unless the automation solution is deployed at a highly critical or responsive operation.
Integration. Prioritize automation solutions that do not require significant integration with IT infrastructure (in other words, stand-alone solutions). This will reduce the implementation complexity, staff time, and effort that needs to be dedicated to the development of an automation solution.
Compatibility. Ensure that your stand-alone solutions can communicate with each other and that their components can be effortlessly combined. Focus on widely accessible technologies with standard interfaces (such as Wi-Fi protocols, APIs, standard data formats, and standard wiring connectors). This decreases the cost of enabling future technology solutions to work together and increases flexibility for adapting the operations.
Modularity. Keep in mind that a rigid automation system (that is, one with all components tightly connected) is difficult to scale and adapt. Build modularity by using technology components that can be replaced or upgraded without severely disrupting the whole process.
For each of these factors, the framework highlights the path to lower automation costs, as represented by the red line in the figure. In this regard, the framework helps identify trade-offs between cost and functionality.
Assessing Automation Costs and Trade-Offs
Let’s look at an example of how to use the framework as a tool to determine whether a solution can be designed or acquired at a low cost. A medium-sized logistics service provider in Boston was interested in implementing a condition-based predictive maintenance solution. The solution was aimed at detecting anomalies in truck component performance, thereby enabling maintenance checks before a breakdown could occur. The company received a proposal from an automation provider for a solution involving sensors and a proprietary algorithm. The logistics provider used the framework to define its requirements and compare them against what the vendor offered, considering each factor in turn.
- Reliability: The company set the level of reliability required at a medium level because some downtime could be tolerated. The vendor solution offered 24/7 monitoring, a higher level of reliability than the company needed.
- Customization: While different vehicles might require different sensors, the company wanted a common algorithm and dashboard across the fleet, so only a medium level of overall solution customization was needed. The provider’s solution, however, varied the feature set by vehicle type, meaning adoption would impose more customization than the company required.
- Integration: The company was seeking a stand-alone solution — one that would, at present, interact only with its vehicles and end users. Consequently, the use case called for a low level of integration, but the vendor offered a solution that required full integration with corporate systems.
- Compatibility: The company considered it likely that, in the future, the solution would need to exchange data with other systems that track additional aspects of vehicle usage, so having compatible components was very important. The solution offered used widely adopted, open IoT standards, aligning with this requirement by easing future data exchange.
- Modularity: Because the fleet was expected to grow, the company wanted a highly modular configuration so it could easily expand or upgrade the solution. But the proprietary solution was seen as having low modularity, with costs mounting as the company added more assets to monitor.
Two important findings emerged from this analysis. First, the required levels for most of the automation design factors corresponded to a low or moderate cost (the green circles in our figure). This suggested that the solution could be designed and implemented internally at a reasonable cost if the company opted for this option. Second, the attributes of the solution offered by the provider either exceeded what was needed or fell short of some requirements the company considered important. That insight enabled the SME to steer its negotiations with the provider, ultimately getting to a lower price by eliminating unnecessary features and selecting those that were truly essential.
We anticipate that the digital divide between SMEs and large companies will continue to grow as the latter heavily invest in automation and AI. It’s important that SMEs understand how they can tap automation technologies affordably in order to maintain competitiveness. If they do so, they will be better positioned to seize new opportunities, improve efficiency, and secure their place in the evolving digital economy.
References
1. J. Macias-Aguayo, D. McFarlane, B. Schönfuß, et al., “A Catalogue of Digital Solution Areas for Logistics SMEs,” IFAC-PapersOnLine 55, no. 10 (2022): 1828-1833, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ifacol.2022.09.664; and B. Schönfuß, D. McFarlane, G. Hawkridge, et al., “A Catalogue of Digital Solution Areas for Prioritising the Needs of Manufacturing SMEs,” Computers in Industry 133 (December 2021): 1-9, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compind.2021.103532.
2. C. Dube, “The Cost of Automated Storage & Retrieval Systems: ASRS Prices & Contributing Factors,” Kardex (blog), updated Jan. 20, 2025, www.kardex.com; and “How Much Does Warehouse Automation Cost?” Pio (blog), accessed May 1, 2025, https://pio.com.
3. “How Small & Medium-Sized Manufacturers Can Start Digitalising: An Industry Example,” video, featuring C. Mayoh, created by Shoestring Digital Manufacturing, posted Nov. 2, 2022, by Institute of Manufacturing, YouTube, 3 min., 9 sec., www.youtube.com.
4. D. McFarlane, S. Ratchev, L. de Silva, et al., “ Digitalisation for SME Manufacturers: A Framework and a Low-Cost Approach,” IFAC-PapersOnLine 55, no. 2 (2022): 414-419, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ifacol.2022.04.229.
5. M. Dhada, J. Macias-Aguayo, A. Mukherjee, et al., “Low-Cost Very Narrow Aisle Pallet Racking Vehicle Utilisation Monitoring Solution,” in IET Conference Proceedings (Stevenage, U.K.: The Institution of Engineering and Technology, October 2023), 144-149, https://doi.org/10.1049/icp.2023.1746.
6. M.J. Saenz, I. Borrella, and E. Revilla, “Digital Supply Chain Transformation: Aligning Operations and Strategy,” Supply Chain Management Review (March-April 2022): 40-47.








